In the low-temperature zone, thermal energy storage represents a technical solution adapted to industrial cooling and air conditioning systems.
Thermal storage is a well-developed technology for low-temperature and high-temperature applications. In the low-temperature zone, thermal energy storage represents a technical solution adapted to industrial cooling and air conditioning systems.
Thermal Storage application
In industrial refrigeration systems such as dairies, breweries etc., cooling loads often peak at a level two or more times higher than the daily 24-hours average load. Some industrial processes also have load peaks or spikes that rise much higher than the average load. In addition, many electric utilities impose demand charges based on the customer’s highest power demand during on-peak hours and/or the entire billing cycle.
Traditional refrigeration systems are designed to satisfy the peak cooling demand, which occurs only a few hours per day. The thermal storage system, which is suitable for any air-conditioning system or refrigeration plant, allows installed chiller capacity (and size of other components) to be significantly reduced – typically between 40 percent and 60 percent. The thermal energy storage systems provide a shortfall of energy when demand exceeds the chiller’s capacity. Thus, the chiller’s operation is continuous, and its efficiency is maximum. This is the most effective way to reduce operating costs of process refrigeration and building air-conditioning, take advantage of the lower cost-off peak electricity, and reduce the demand charge by reducing the required electrical supply.
With such benefits available from the low-temperature thermal energy storage, it has been used as a component of central AC systems where the peak load occurs only for some hours during the daytime. The provision of such systems is also beneficial where there is a concessional power tariff during the night hours. These systems are estimated to be employed in about 20 to 25 percent of the central chilled water AC Systems.
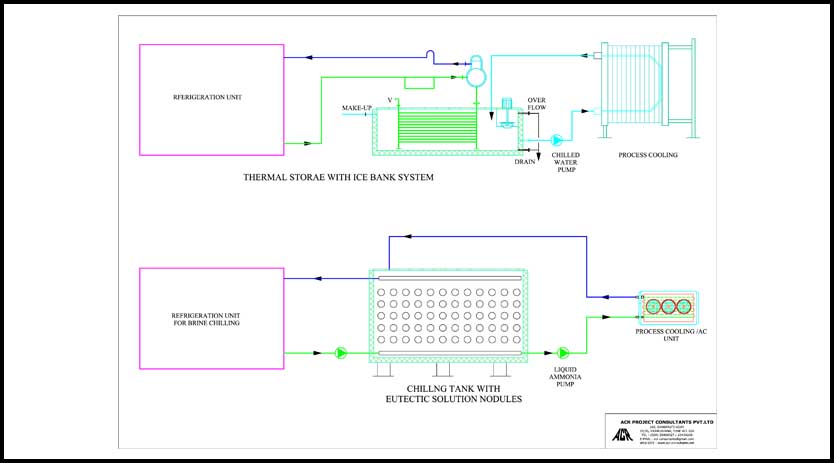
In applications like dairies, the peak food of Milk chilling & pasteurisation occurs during morning and evening hours. These systems have been commonly used for the benefits stated.However, it must be noted that the process involves freezing water in ice bank tanks or other phase change material filled in nodules stored in the chilling brine tanks. And the refrigeration system needs to operate at 60 to 800C lower evaporative temperatures than direct chilling systems. This results in an increased energy consumption per unit of refrigeration required. The current trend is to use systems with falling film chillers, which can operate at higher evaporative temperatures with lower temperature differences than conventional systems for direct operational loads.
Thermal Storage Materials
Thermal storage materials are selected as per application temperature requirements. The most explicit material is water, in which the energy can be stored in ice. For lower temperature brine, glycol (mono ethylene or mono propylene) or other eutectic solutions are used.
The energy storage is done by freezing the mediums mentioned above, thus making use of the latent heat of freezing, which has a very high energy density (6 to 12 times) compared to the sensitive energy storage with a much smaller storage volume.
For very high-temperature applications, such as storing high-temperature solar energy, molten metal has been used in a project in California.
Effect of temperature control on foods
Perishable foods are different types, viz. fruits and vegetables, dairy products, poultry, fisheries, meat products and some ready-to-eat foods etc. F&V products make up the major share of perishable foods. They continue the physiological functions and chemical µ microbiological changes after harvesting resulting in loss of moisture quality, taste etc. Cooling the product within a short time after harvesting helps reduce various activities mentioned above and helps prevent loss of quality, thus, enhancing its life and retaining the quality.
In modern systems, the produce is transported to the pack houses where operations like sorting, washing, drying, grading and packing are carried out. Further, the product is pre-cooled fast, within 4 to 6 hours, in a pre-cooling chamber to the required temperature and high RH. The pre-cooled product pallets are then kept in the staging cold store for a short time before dispatching to the distribution centre or food stores. The desired pre-cooling temperature for various products is given in ASHRAE, ISHRAE & WFLO handbooks. Similarly, other food items undergo the process of chilling, freezing, and storage as per the standard practice. The frozen foods are stored in the temperature range from (-) 180C to (-) 250C or lower as required.Thus, the chilling and freezing process saves perishable foods and makes the distribution up to the consumer through the cold chain.
Thermal Control Sensors
Various thermal sensors are used to control a system’s temperature, product, etc. They are Resistance temperature detectors (RTD), Thermocouples, Thermistors, Thermometers, Semiconductor thermal sensors etc. IoT devices grew during the reefer vans phase.
Use of IoT Devices
IoT (Internet of Things) for cold chain logistics ensures delivery of long-distance food, perishable products, medicines etc., with assured freshness and quality. IoT devices Like Temperature sensors (RTD, Temperature Transmitter) are used on reefer vans, Rail cargo etc., to monitor the temperature of food items during transport. The sensors gather and share this data in real-time. This ensures things stay at optimum temperature, thereby increasing longevity. IoT solutions require minimum human intervention.
All the data collected by IoT devices is analysed with other devices in real time. This gets notified of any issues emerging in the transportation process. Managers can take quick decisions to fix these issues and ensure food quality. The data collected by the IoT device can be used to generate reports by the software on the device.
This has many benefits like increasing efficiency and maintenance of quality, reducing operational cost, and reducing spoilage of foods etc.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.